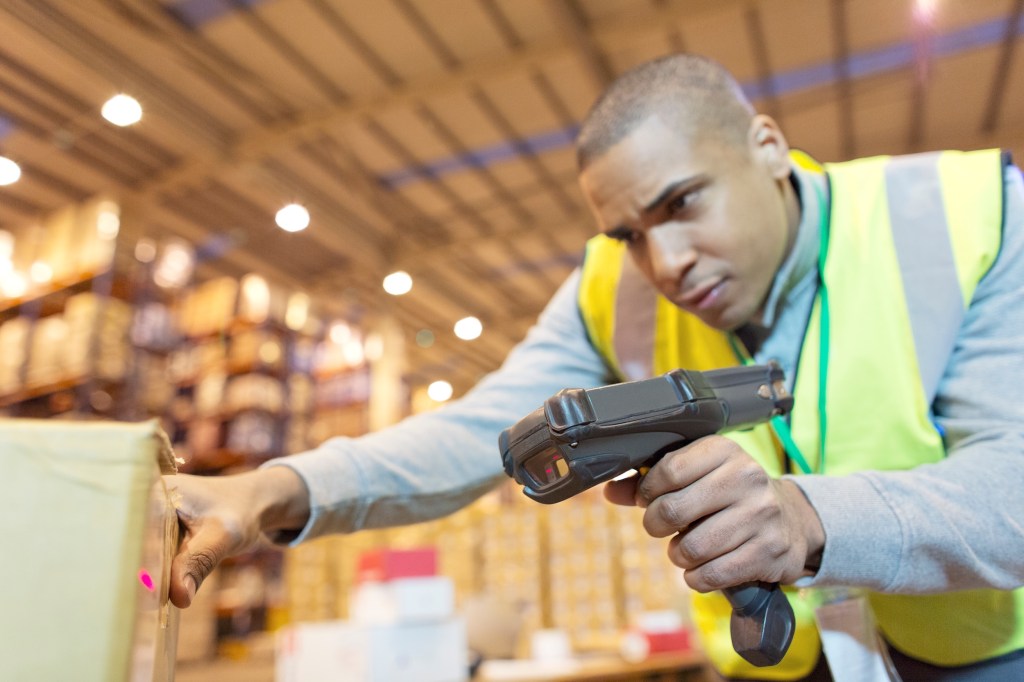
In the fast-moving world of ecommerce, accuracy and efficiency aren’t optional; they’re expected. As order volumes grow and supply chains become more complex, scanning systems have become essential for ecommerce brands looking to scale smoothly.
But what do these systems actually do, and how can you put them to work in your own operation? These behind-the-scenes tools play a crucial role in keeping inventory data accurate, speeding up fulfilment, and minimising costly errors.
In this guide, we’ll break down the core components of warehouse scanning systems, walk through best practices for implementation, and share practical tips and proven strategies to drive greater speed, accuracy, and control across your warehouse.
What are warehouse scanning systems?
A warehouse scanning system is an integrated combination of hardware and software that digitizes inventory tracking throughout the supply chain.
These systems capture critical data points such as product location, SKU details, and inventory counts to provide real-time visibility into warehouse operations, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and optimise their processes.
Warehouse scanning systems also:
- Significantly reduce errors and improve efficiency.
- Automate data capture to eliminate the need for time-consuming and error-prone manual data entry.
- Reduce the risk of stockouts, overstocking, and other costly mistakes.
- Enable proactive inventory management and a seamless customer experience across multiple touchpoints.
Types of warehouse scanner hardware
Warehouse scanning systems rely on a variety of hardware options to capture data efficiently and accurately. Different scanner types serve various warehouse environments and operational needs, and selecting the right hardware involves considering factors such as durability, scan range, mobility, and battery life.
Handheld scanners
Handheld scanners are the most common type of scanning hardware used in warehouses. They come in various configurations, including 1D and 2D scanners, as well as laser and imager-based models.
Standard handheld scanners are ideal for close-range scanning, while long-range models can capture barcodes from greater distances, making them suitable for scanning items on high shelves or in hard-to-reach locations.
Connectivity options for handheld scanners include Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and cellular, each of which impacts the speed and reliability of real-time data transmission.
When selecting handheld scanners, key features to look for include durability to withstand drops and harsh environments, long battery life to minimise downtime, and ergonomic design to reduce worker fatigue during extended use.
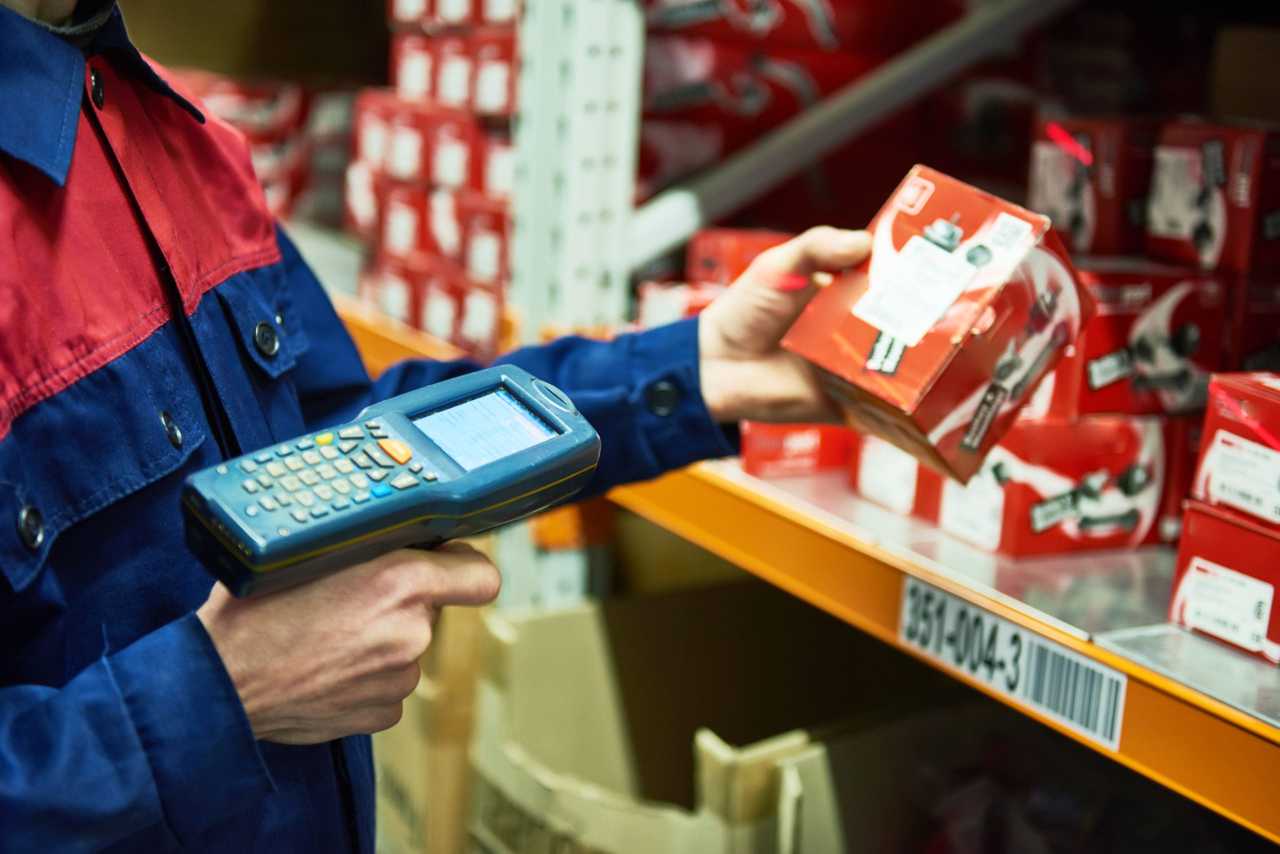

Wearable scanners
Wearable scanning technology has gained popularity in recent years due to its ability to improve worker productivity through hands-free operation.
Wearable options include ring scanners, wrist-mounted units, and voice-directed headsets. These devices allow workers to keep both hands free for picking and handling products, reducing the time and effort required to switch between tasks.
Wearable scanners are particularly beneficial in high-volume picking scenarios, where they can significantly improve ergonomics and reduce worker fatigue. By eliminating the need to constantly reach for and aim a handheld device, wearable scanners can increase picking speed and accuracy.
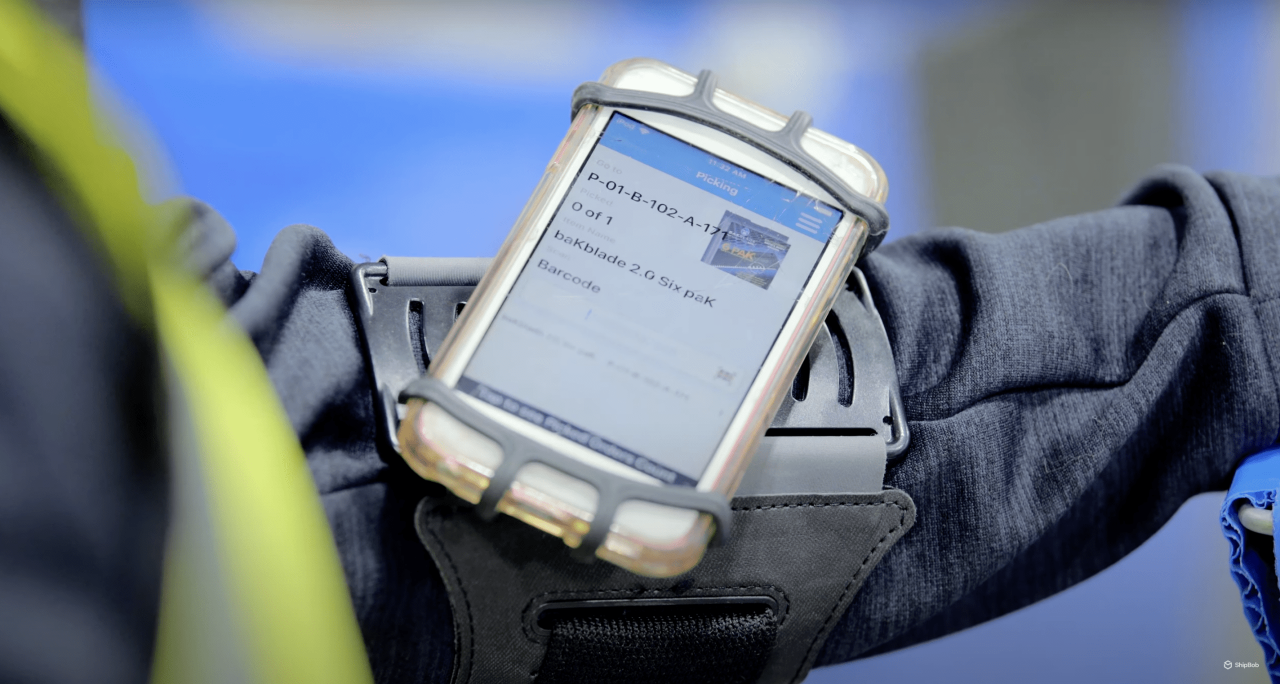

Fixed-position scanners
Fixed-position scanners are designed for automated environments, such as conveyor systems and packing stations.
These scanners are mounted in a stationary position and automatically capture barcodes as items pass by. Fixed scanners often feature omnidirectional scanning capabilities, allowing them to read barcodes from any angle, making them ideal for high-throughput operations.
Integrating fixed scanners with conveyor lines, sortation systems, and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) enables touchless verification at key points in the fulfilment process. In eliminating the need for manual scanning, fixed-position scanners can significantly increase the speed and accuracy of automated workflows, reducing the risk of errors and bottlenecks.
RFID scanning systems
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) scanning systems offer advanced capabilities beyond traditional barcode scanning.
RFID technology uses radio waves to communicate between tags attached to items and readers that capture the tag data. RFID tags can be passive (powered by the reader’s signal) or active (battery-powered), and they can store more information than standard barcodes.
One of the key advantages of RFID scanning is its ability to capture data from multiple items simultaneously without requiring a direct line of sight. This enables bulk scanning of entire pallets or cases, significantly reducing the time required for inventory counting and verification. RFID technology is particularly valuable for tracking serialized or high-value items, as it allows for item-level visibility and traceability throughout the supply chain.
Key warehouse scanning workflows
Warehouse scanning systems play a vital role in creating a digital thread that connects all aspects of warehouse operations.
Here are some of the key workflows that benefit from scanning technology and how each one builds upon the previous step to create a seamless, accurate, and transparent operation.
Receiving and putaway
The receiving process is the first opportunity to establish inventory accuracy through scanning. By scanning incoming products against purchase orders or warehouse receiving orders (WROs), businesses can quickly identify discrepancies and prevent downstream issues.
Directed putaway processes, guided by scanning technology, ensure that products are stored in optimal locations based on factors like velocity, size, and product affinity. Proper receiving scans lay the foundation for accurate inventory management and streamlined operations.
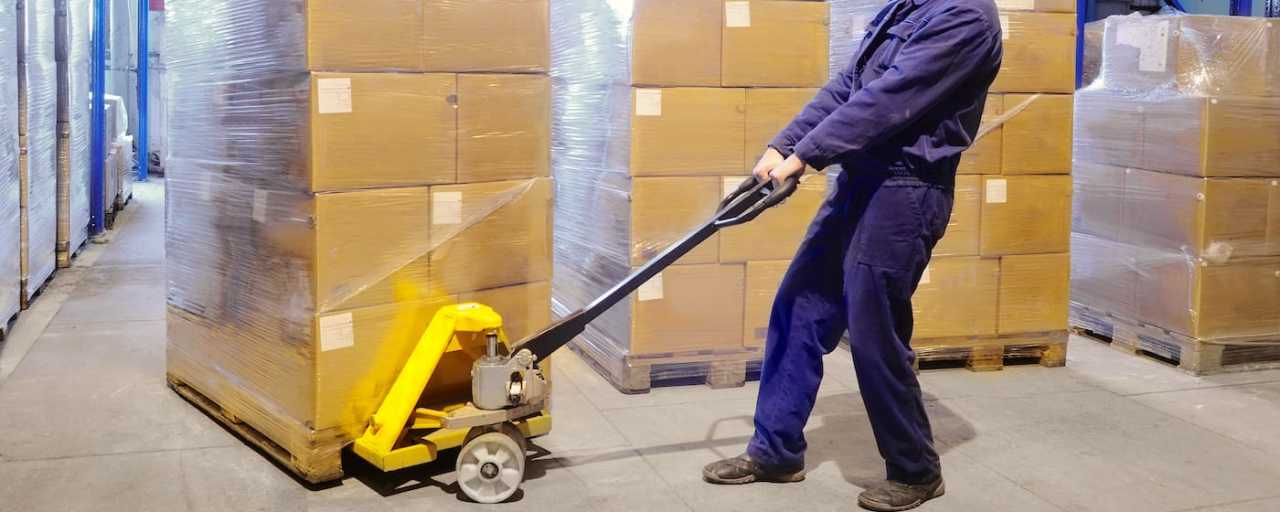

Inventory management and cycle counting
Regular scanning is essential for maintaining inventory accuracy without requiring full warehouse shutdowns.
Implementing cycle counting programs based on ABC classification lets businesses prioritize the scanning of high-value or fast-moving items. This approach enables perpetual inventory systems that continuously update stock levels as transactions occur.
With scanning technology, cycle counts become more efficient and accurate, reducing the need for time-consuming physical inventories.
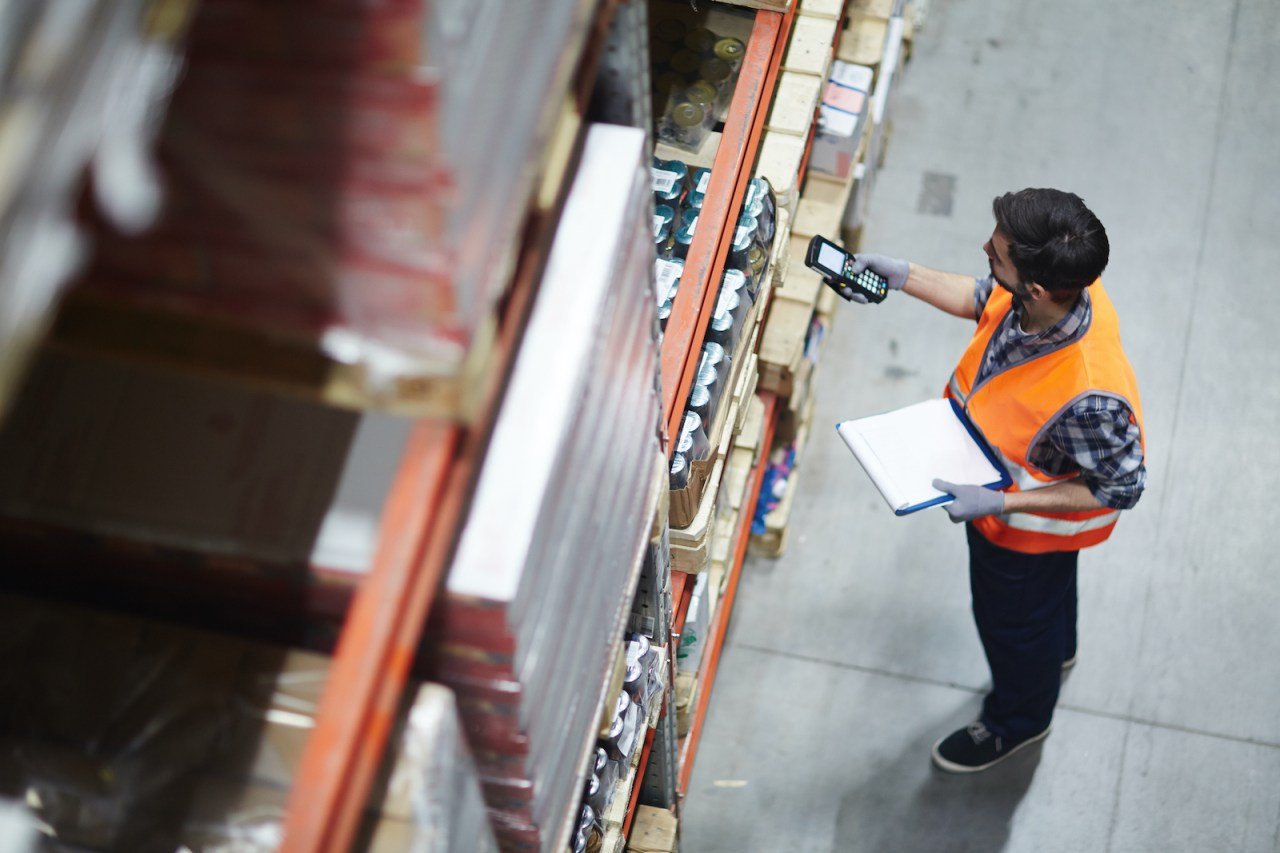

Order picking strategies
Scanning systems play a crucial role in ensuring accurate order fulfilment. These systems confirm the right item, quantity, and location during picking, which minimises errors and improves customer satisfaction.
Different picking methodologies, such as single order, batch, zone, and wave picking, can be enhanced through scanning technology. For example, batch picking with scanning enables the simultaneous fulfilment of multiple orders, while still maintaining accuracy through barcode verification.
Specialized workflows, like case picks versus unit picks, can also be optimised through scanning, ensuring the right product configuration is selected for each order.

Packing verification
The packing stage represents the final opportunity to catch errors before orders leave the warehouse. When brands incorporate scanning into the packing process, they can verify that the right items are included in each shipment.
Weight verification systems, integrated with scanners, provide an additional layer of accuracy by comparing the actual weight of the package to the expected weight based on the scanned items.
Scanning at pack stations can also trigger automated label printing, streamlining the process and reducing the risk of manual errors.
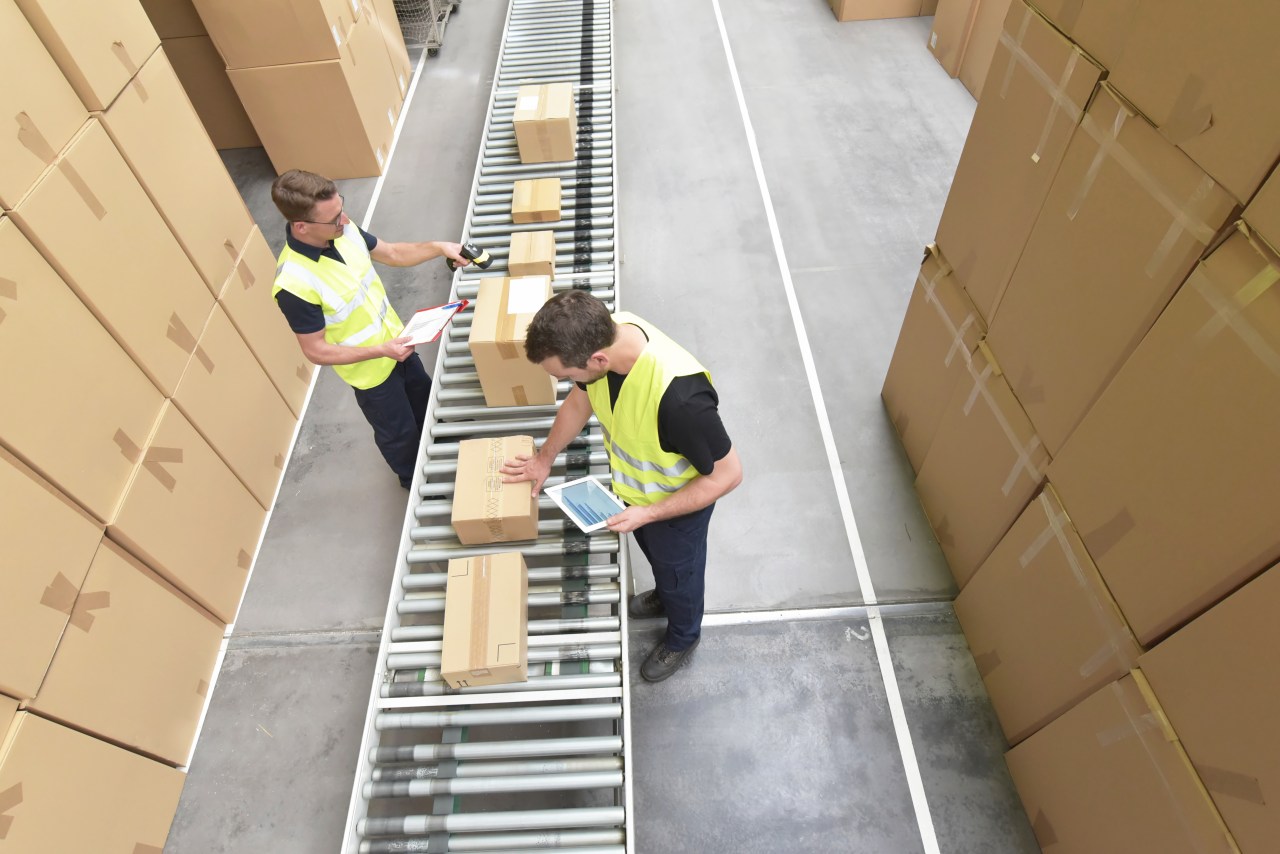

Shipping and courier integration
Scanning systems play a vital role in connecting internal warehouse operations with external shipping couriers. By scanning outbound packages, businesses can automatically transmit tracking information to couriers and provide real-time updates to customers.
This integration also enables features like automated rate shopping and service selection, ensuring that orders are shipped via the most cost-effective and efficient method. Cross-courier standardization through scanning systems simplifies the shipping process and provides a consistent experience for customers, regardless of the courier used.

Returns processing
Efficient returns processing is critical for maintaining inventory accuracy and customer satisfaction.
Brands that implement scannable return merchandise authorizations (RMAs) streamline the returns process and quickly update inventory levels. When a returned item is scanned, the system can automatically determine the appropriate disposition, such as restocking, refurbishing, or discarding.
This scanning-based approach minimises the risk of errors and ensures that returned items are promptly processed and made available for resale if appropriate.

Warehouse scanning software essentials
Scanning hardware is only one part of the equation when it comes to optimising warehouse operations. The software that powers these devices is equally important, turning raw scan data into actionable insights and enabling seamless integration with existing systems.
When evaluating scanning software, look for solutions that offer user-friendly interfaces, real-time data synchronization, and flexible configuration options.
Cloud-based vs. on-premise solutions
One of the first decisions to make when selecting scanning software is whether to opt for a cloud-based or on-premise solution.
| Cloud-based | On-premise | |
| Key Factors | Lower upfront costs Automatic updates Offer access data from anywhere with an internet connection | Provide greater control over data security Can be customised to meet specific business requirements Often require more IT resources to maintain Can be less scalable than cloud-based systems |
| Ideal For | Businesses with multiple warehouse locations or remote teams | Companies with strict compliance needs or limited internet connectivity |
Mobile device management (MDM)
As businesses deploy more scanning devices across their warehouses, managing these assets becomes increasingly complex. Mobile device management (MDM) software simplifies this process by providing a centralised platform for deploying, securing, and maintaining scanner fleets.
With MDM, IT teams can remotely configure devices, push software updates, and troubleshoot issues without physically handling each scanner. This minimises downtime and ensures that all devices are running the latest versions of critical applications.
MDM also helps enforce security policies, such as password requirements and data encryption, protecting sensitive business information.
Low-cost and open-source alternatives
For smaller businesses or those with limited budgets, there are several low-cost and open-source alternatives to enterprise-grade scanning software. Smartphone-based scanning apps, for example, can turn any mobile device into a basic barcode scanner.
While these solutions may lack advanced features, they can be an effective entry point for businesses just starting to digitize their warehouse operations.
When evaluating low-cost or free software options, consider factors such as ease of use, compatibility with existing systems, and community support. Open-source solutions may require more technical expertise to implement but offer greater customisation possibilities and freedom from vendor lock-in.
🔌 Integrating scanning systems with WMS and ERP
To fully realize the benefits of warehouse scanning technology, it’s essential to integrate these systems with your existing warehouse management system (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software.
Real-time data synchronization
One of the key advantages of integrating scanning systems with WMS and ERP is the ability to synchronize data in real-time. As items are scanned during receiving, picking, packing, and shipping processes, the information is instantly updated in the corresponding software modules.
This real-time visibility enables managers to make proactive decisions based on accurate inventory data, such as adjusting stock levels or reallocating resources to meet demand.
To achieve this level of synchronization, it’s important to minimise latency between the moment a scan occurs and when the data is reflected in the database.
Look for scanning solutions that offer robust APIs and support industry-standard protocols like REST and SOAP to ensure fast and reliable data transfer.
Integration with popular platforms
Many businesses rely on popular ecommerce platforms like Shopify, Magento, or WooCommerce to manage their online sales channels. Integrating warehouse scanning systems with these platforms can streamline order fulfilment processes and provide customers with real-time updates on their shipments.
When selecting a scanning solution, consider its compatibility with your existing ecommerce stack. Some providers offer pre-built connectors or plugins that simplify integration, while others may require custom development work.
If you’re using a less common platform or have highly specialized requirements, look for scanning vendors that provide comprehensive API documentation and support.
Migrating from legacy systems
For businesses with older warehousing systems, migrating to a modern scanning solution can be a daunting prospect. Legacy platforms may rely on proprietary hardware or software that is difficult to integrate with newer technologies. Additionally, staff may be resistant to change, particularly if they’ve been using the same processes for years.
To overcome these challenges, consider a phased approach to migration that minimises operational disruptions. Start by identifying the most critical scanning workflows and prioritize those for initial implementation. As staff become more comfortable with the new system, gradually expand its use to other areas of the warehouse.
It’s also important to address backward compatibility concerns when selecting a scanning solution. Look for vendors that offer support for legacy hardware and software, or consider investing in middleware that can bridge the gap between old and new systems.
Custom workflow configuration
Every warehouse operation is unique, with its own set of processes, products, and performance metrics. To fully optimise your scanning workflows, it’s essential to have the ability to customise the software to meet your specific needs.
Some scanning solutions offer low-code or no-code configuration options, allowing non-technical users to adapt the system without extensive programming knowledge. This can be particularly useful for businesses that need to frequently adjust their processes in response to changing market conditions or customer requirements.
When evaluating scanning software, look for solutions that provide a balance of out-of-the-box functionality and customisation options. The ideal system should be easy to set up and use for common workflows while still providing the flexibility to adapt to your unique business needs.
How to implement your own warehouse scanning system
Implementing a warehouse scanning system can be a complex undertaking, but with careful planning and execution, it can deliver significant benefits to your operation. Here’s a roadmap to help guide you through the process.
1. Assess your current state
Before embarking on a scanning implementation project, it’s important to take stock of your current processes and identify areas for improvement.
Start by mapping out your existing workflows, from receiving to shipping, and note any manual or paper-based steps that could be automated with scanning technology.
Next, conduct a readiness assessment to determine whether your organisation has the necessary infrastructure and resources to support a scanning system. This may include evaluating your network connectivity, hardware compatibility, and staff technical skills.
2. Building your requirements document
Once you have a clear understanding of your current state and improvement opportunities, it’s time to build a comprehensive requirements document for your scanning system.
This document should outline your key objectives, functional requirements, and technical specifications.
Start by prioritizing your requirements into “must-haves” and “nice-to-haves.” This will help you focus on the most critical features during the vendor selection process. Be sure to involve stakeholders from across the organisation, including warehouse staff, IT, and management, to ensure that all perspectives are considered.
3. Start selecting vendors
With your requirements document in hand, you’re ready to begin evaluating scanning system providers.
Start by researching vendors that specialize in your industry or have experience with similar warehouse operations. Look for providers that offer a range of hardware and software options to meet your specific needs.
When engaging with potential vendors, be sure to ask for live demonstrations of their products and request references from existing customers. This will give you a better sense of how the system performs in real-world scenarios and how responsive the vendor is to customer needs.
If possible, consider conducting a pilot program with your top vendor choices before committing to a full implementation. This will allow you to test the system in your own environment and gather feedback from end users.
4. Establish implementation timeline and milestones
Once you’ve selected a vendor, it’s time to plan out your implementation timeline. Work with your vendor to establish key milestones and deliverables, such as hardware installation, software configuration, and user training.
Be sure to allocate sufficient time for testing and quality assurance before rolling out the system to the entire warehouse. This will help identify any issues or bugs early on and minimise disruptions to your operations.
Throughout the implementation process, maintain open communication with your vendor and internal stakeholders. Regular status updates and progress reports will help keep everyone aligned and ensure that the project stays on track.
5. Train staff and apply change management
One of the most critical aspects of a successful scanning system implementation is user adoption. To ensure that your staff are comfortable and proficient with the new technology, invest in comprehensive training programs that cover both the hardware and software components of the system.
Consider a variety of training formats, such as in-person workshops, online tutorials, and hands-on practice sessions, to accommodate different learning styles. Provide ongoing support and refresher training to reinforce best practices and address any questions or concerns that arise.
In addition to training, it’s important to manage the organizational change that comes with implementing a new system.
- Communicate the benefits of the scanning technology clearly and often.
- Involve staff in the planning and implementation process to build buy-in.
- Celebrate successes along the way and recognise individuals or teams that embrace the new technology and drive positive results.
By making the scanning system an integral part of your warehouse culture, you’ll be better positioned to realize its full potential.
💵 Cost considerations and ROI calculation
Implementing a warehouse scanning system requires a significant investment of time, resources, and capital.
To ensure that you’re making a sound financial decision, it’s important to carefully consider all of the costs involved and calculate the potential return on investment (ROI).
Hardware investment strategies
One of the most significant expenses associated with a scanning system is the hardware itself. Depending on the size of your operation and the types of devices you require, this can quickly add up.
When evaluating hardware options, consider both the upfront purchase price and the total cost of ownership over the life of the equipment. This includes factors such as maintenance, repairs, and battery replacement.
For smaller operations or those with limited capital budgets, refurbished equipment can be a cost-effective alternative to buying new. Many vendors offer certified pre-owned devices that have been thoroughly tested and come with warranties.
Leasing is another option to consider, particularly if you need to scale your scanning capabilities quickly or want to avoid a large upfront investment. Leasing allows you to spread the cost of the equipment over time and can often include maintenance and support services.
Software licensing models
In addition to hardware costs, you’ll also need to factor in the expense of scanning software. Licensing models can vary widely depending on the vendor and the specific features and capabilities you require.
Some vendors offer perpetual licenses, which provide unlimited use of the software for a one-time fee. Others use a subscription-based model, where you pay a recurring fee (usually monthly or annually) for access to the software and support services.
When evaluating software options, consider the total cost of ownership over the expected life of the system. This includes not only the initial licensing fees but also any ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and support costs.
It’s also important to understand how the licensing model scales with your business. Some vendors charge per device, while others use a concurrent user model that allows for a set number of users to access the system simultaneously. Choose a model that aligns with your current needs and provides room for growth as your operation expands.
Implementation and training costs
Another often-overlooked expense when budgeting for a scanning system is the cost of implementation and training. Depending on the complexity of your operation and the level of customisation required, this can be a significant portion of the overall project cost.
Implementation costs may include expenses such as:
- Hardware installation and configuration
- Software setup and integration with existing systems
- Custom development work to adapt the system to your specific needs
- Data migration from legacy systems
- Project management and consulting fees
Training costs will depend on the size of your team and the depth of knowledge required. Consider expenses such as instructor fees, course materials, and the time staff will spend away from their regular duties to attend training sessions.
To minimise implementation and training costs, look for vendors that offer comprehensive documentation, online resources, and pre-configured templates or workflows that can be easily adapted to your needs. Investing in thorough training upfront can also help reduce the need for ongoing support and rework down the line.
Calculating return on investment
With a clear understanding of the costs involved, you can begin to calculate the potential ROI of your scanning system. This involves comparing the expected benefits of the system (such as increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved customer satisfaction) against the total cost of ownership.
To calculate ROI, start by estimating the quantifiable benefits of the scanning system. This may include metrics such as:
- Labor savings from reduced manual data entry and improved productivity
- Cost savings from reduced inventory shrinkage and fewer mis-ships
- Increased revenue from improved order accuracy and faster fulfilment times
Next, determine the total cost of the system over a set period (usually 3-5 years). This should include all of the expenses outlined above, such as hardware, software, implementation, and training costs.
Finally, use the following formula to calculate ROI:
ROI = (Total Benefits – Total Costs) / Total Costs x 100
For example, if you expect a scanning system to deliver $500,000 in benefits over three years and the total cost of the system is $300,000, the ROI would be:
ROI = ($500,000 – $300,000) / $300,000 x 100 = 67%
In addition to the quantifiable benefits, consider the intangible advantages of a scanning system, such as improved customer satisfaction, better data visibility, and increased employee morale. While these may be more difficult to measure, they can have a significant impact on the long-term success of your business.
How ShipBob’s fulfilment services simplify warehouse scanning implementation
Implementing a warehouse scanning system can be resource-intensive. But, with ShipBob, it doesn’t have to be. As an expert supply chain enablement partner, ShipBob brings scanning best practices, proven workflows, and enterprise-grade infrastructure to your fulfilment operation from day one.
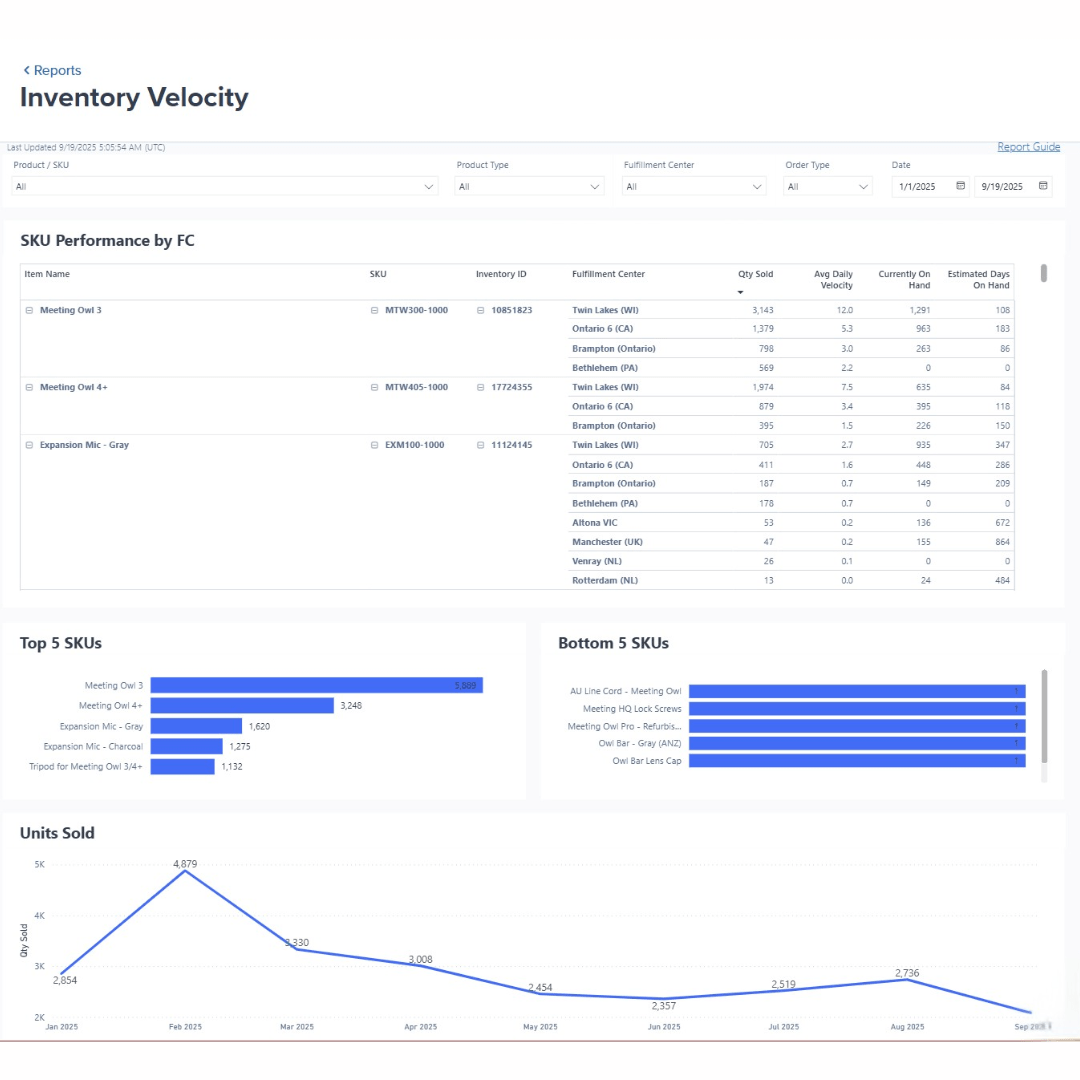
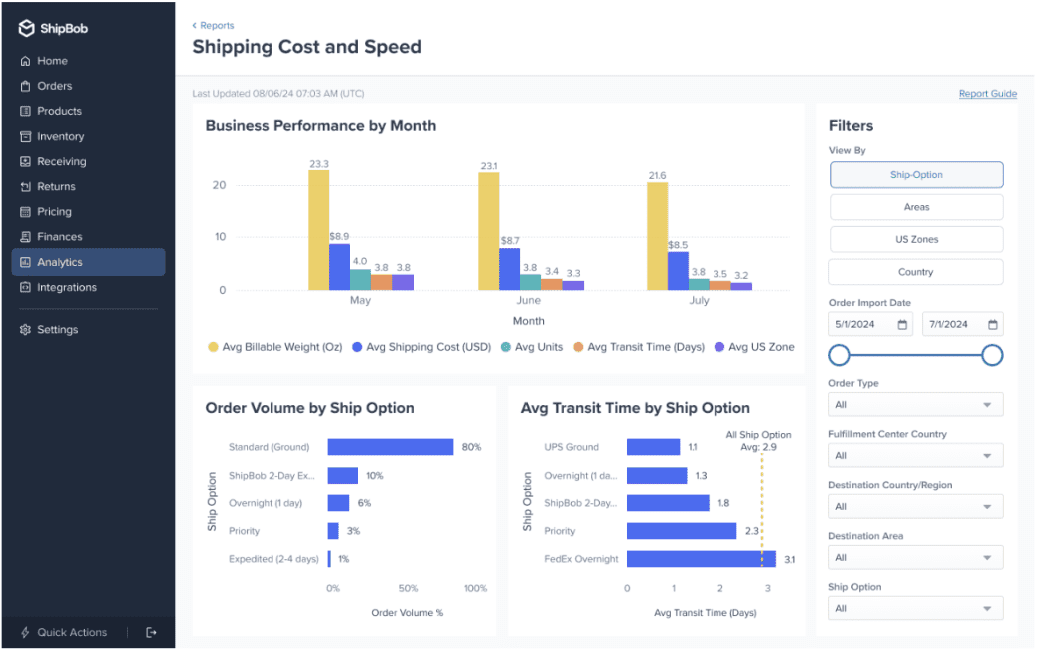
Every ShipBob fulfilment centre is equipped with modern scanning technology that tracks inventory at every touchpoint, from receiving and putaway to picking, packing, and shipping. This system not only reduces human error but also ensures real-time inventory accuracy, which is essential for meeting customer expectations and maintaining stock visibility across channels.
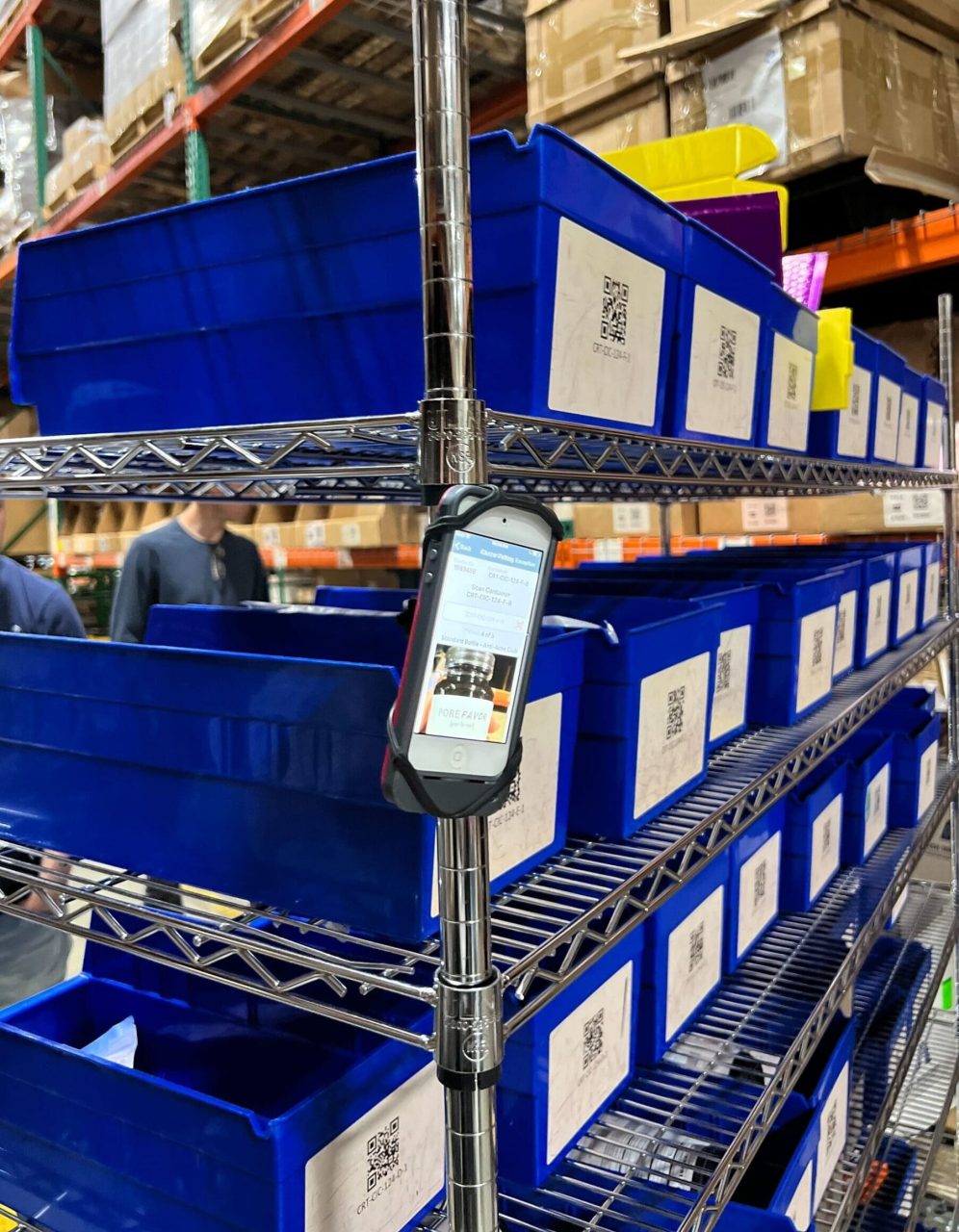

What’s more, ShipBob’s platform seamlessly integrates with your ecommerce store and back-end systems, giving you end-to-end transparency without the heavy lift of building and maintaining your own scanning infrastructure.
“Integrating ShipBob’s WMS into our Miami warehouse has really helped our in-house business on so many levels. It did wonders for our inventory accuracy—having a system that would decrement inventory in real-time based on shipments gave us a lot more insight into our inventory movement and made our inventory counts in different fulfilment stages much more reliable.
Before ShipBob, we used to do a lot of that tracking and updating manually and it was a lot more work for our team as well, so automating everything through ShipBob’s WMS has been very helpful. Also with the amount of sales volume that we drive, we have to nail our inventory tracking across the entire supply chain.”
Rachel Tannenholz, President, and Melissa Mosheim, Director of Logistics at Aroma360
With built-in tools like inventory tracking, order status updates, and analytics, you get all the benefits of a scanning-enabled warehouse (without the implementation headaches).
By partnering with ShipBob, you can skip the cost and complexity of DIY system rollouts and tap into a fulfilment network that’s already optimised for accuracy, speed, and scale.
Whether you’re looking to outsource logistics entirely or enhance your existing setup, ShipBob makes it easy to put powerful scanning systems to work (and keep your business moving forward).
For more information about how ShipBob can help you optimise your warehouse operations, click the button below to get in touch.
Warehouse scanning systems FAQs
Here are answers to some of the most common questions about warehouse scanning systems.
What is the best warehouse scanner system for small businesses?
For small businesses, the best warehouse scanner system should balance affordability with scalability. Entry-level solutions like smartphone-based scanning apps can provide a cost-effective starting point, while dedicated handheld scanners offer more durability and performance as operations grow. Look for systems with flexible pricing models and modular components that can adapt to changing needs.
When evaluating software, prioritize user-friendly interfaces and seamless integration with existing platforms like Shopify or Amazon. Cloud-based solutions often provide the best balance of accessibility and scalability for growing businesses.
How do I choose between 1D and 2D barcode scanners?
The choice between 1D and 2D barcode scanners depends on your specific use cases and future requirements. 1D scanners are suitable for most basic inventory tracking needs, while 2D scanners offer more advanced capabilities like capturing images and reading QR codes.
If your products require more complex data encoding or you anticipate needing to scan 2D barcodes in the future, investing in 2D scanners can provide long-term value. Industries like healthcare and electronics manufacturing often require 2D scanning for serialized tracking and traceability.
Can I integrate scanners with my existing WMS or ERP?
Yes, most modern scanning systems can integrate with existing warehouse management systems (WMS) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms. However, the ease of integration depends on factors like API compatibility, data format standards, and customisation requirements.
When evaluating scanning solutions, ask providers about their experience integrating with your specific WMS or ERP. Inquire about middleware options or custom connectors for complex integration scenarios. Ensure that your IT team is involved early in the process to identify potential challenges and develop a comprehensive integration plan.
How do I calculate ROI for warehouse scanning systems?
To calculate the return on investment (ROI) for a warehouse scanning system, use the following formula:
ROI = (Annual Cost Savings + Annual Productivity Gains – Total System Cost) / Total System Cost
Annual cost savings include direct reductions in labour, error-related expenses, and inventory carrying costs. Productivity gains encompass efficiency improvements in picking, packing, and inventory management processes. Total system cost includes hardware, software, implementation, and training expenses.
What are the most common implementation challenges?
Common challenges during warehouse scanning system implementations include:
- Inadequate wireless network coverage leading to connectivity issues.
- Resistance to change from warehouse staff accustomed to manual processes.
- Insufficient training resulting in low adoption rates and user errors.
- Compatibility issues between scanning hardware and existing software systems.
- Scope creep and budget overruns due to poorly defined requirements.
To mitigate these challenges, develop a comprehensive project plan that addresses infrastructure upgrades, change management strategies, and user training programs. Maintain open communication with stakeholders throughout the implementation process and celebrate quick wins to build momentum.
How does ShipBob’s scanning system ensure inventory accuracy?
ShipBob’s scanning system ensures inventory accuracy through a rigorous multi-point verification process. Upon receiving inbound inventory, each item is scanned and checked against the expected quantity and product details. During the picking process, scanners confirm the correct SKU and quantity before items are placed in the outbound package.
At the packing station, a final scan verifies that the order is complete and accurate before shipping. This multi-step scanning protocol, combined with regular cycle counting, helps ShipBob maintain inventory accuracy across its fulfilment network.
What scanning capabilities should I look for in a 3PL partner?
When evaluating a third-party logistics (3PL) partner’s scanning capabilities, look for the following key features.
- Real-time visibility: Ensure that the 3PL’s scanning system provides immediate updates on inventory levels, order status, and product movements across all locations.
- Advanced scanning technology: Confirm that the 3PL invests in modern scanning hardware and software to support efficient and accurate operations. Inquire about capabilities like RFID, voice-directed picking, and autonomous mobile robots.
- Customizable workflows: Verify that the 3PL can adapt its scanning processes to your unique product and order characteristics. Ensure that they can handle any specialized requirements like batch tracking or serialized inventory management.
- Robust integration: Investigate the 3PL’s ability to seamlessly connect its scanning system with your existing ecommerce platforms, order management systems, and reporting tools.
- Continuous improvement: Assess how the 3PL leverages scan-based data to drive ongoing optimisation of its processes and facilities. A commitment to continuous improvement ensures that your products are handled with increasing efficiency and accuracy over time.




